During a website redesign, re-platform, or area change, it isn’t unusual to see a discount in natural search visitors. The panic usually begins weeks after making an attempt one factor after one other and the visitors doesn’t return.
In this submit, I’m going to stroll you thru a course of I use to speed up the restoration of this painful drawback.
Identify the Root Causes
Instead of operating a website by means of a full search-engine-optimization guidelines, which usually takes a number of beneficial time, I choose to concentrate on the 20 % of glitches which are doubtless inflicting eighty % of the issue. This strategy permits for quicker, incremental restoration, leaving time to deal with the opposite points later.
When natural visitors drops, it’s sometimes brought on by fewer pages performing, or fewer guests per web page, or each. I first attempt to decide which of those is the difficulty. If there are fewer pages performing, there probably are indexing issues. If we’ve got fewer guests per web page, the pages is perhaps weak in content material. If we now have each points, there might be web page status issues — i.e., fewer high quality hyperlinks to the location. Duplicate content material and rancid content material can each dilute web page popularity, as can a hyperlink penalty.
Using this framework, one can isolate the issues which might be possible hurting visitors. Common errors that I’ve seen are:
- Missing, incorrect, or incomplete URL mappings — decrease web page fame;
- Massive URL consolidations resulting in a smaller website — much less content material;
- New infinite crawl areas (defined under) — fewer pages listed;
- New infinite scrolling that isn’t web optimization pleasant — much less content material;
- Backlink penalties — decrease web page status.
And listed here are the important thing locations I shortly gather proof:
- 404 errors in Google Search Console;
- Landing web page natural visitors report in Google Analytics;
- Index standing and XML sitemaps reviews in Google Search Console;
- URL parameters settings in Google Search Console;
- Latest hyperlinks report in Google Search Console.
In the subsequent steps, every potential drawback is a thesis to validate or invalidate. For this, I use knowledge science instruments to organize the proof collected and discover it with knowledge visualization.
The most essential a part of this system is creating the instinct to ask the best questions. Those questions ought to decide what knowledge and proof to gather, and learn how to course of it and visualize it.
What follows is an precise investigation, with actual buyer knowledge, to know this knowledge-pushed framework.
Evidence Collection Example
I lately helped a model-identify retailer throughout a re-platform and redesign undertaking, in preparation for the 2016 vacation season. We began advising the corporate in June, and the brand new website launched firstly of October. But the location began to expertise a downtrend in natural search visitors earlier than then, at the start of September, as yr-over-yr natural visitors was down roughly 20 %.
The shopper hoped to reverse this development with the brand new website design.
We rigorously deliberate every part. We mapped — by way of 301 redirects — all the previous URLs to the brand new ones. We did a number of rounds of testing and evaluate on the staging website.
Note that we didn’t change title tags earlier than the launch. I want to not change title tags throughout redesigns. Instead, I want to vary them a few weeks afterwards. This is as a result of, in my expertise, title tag modifications may end up in re-rankings. So it’s higher to change them in a extra managed trend, so you possibly can roll again the modifications in the event that they don’t enhance efficiency.
But, regardless, a few weeks after the launch, natural visitors dropped even additional, by roughly forty % over the earlier yr. But, fortunately, we did determine the issue.
Using our framework, we requested if we’re dropping pages, guests per web page, or each? We gathered the info after which graphed it, to visualise.
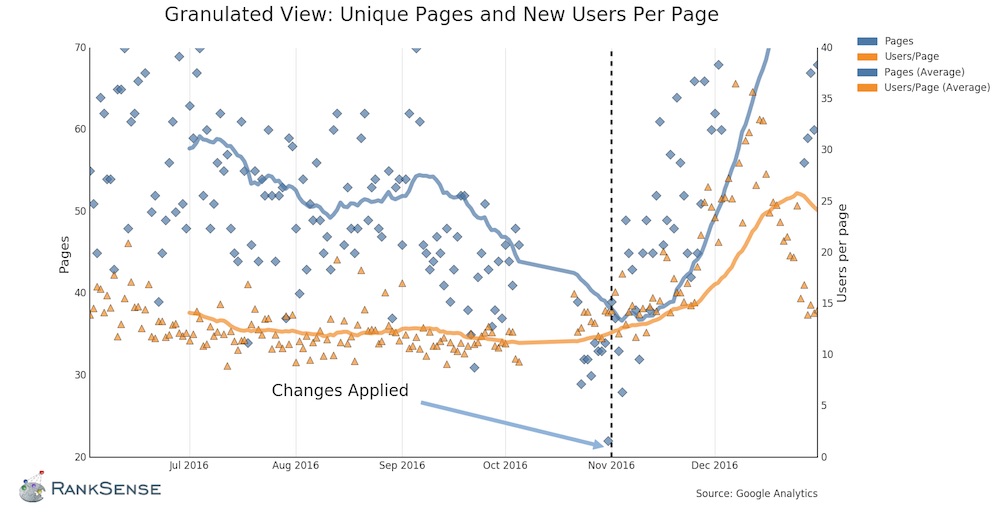
The variety of guests (customers) per web page, proven in yellow within the decrease portion of the graph, remained comparatively fixed. But the variety of pages listed, within the blue line, decreased. Fixing the issue in November 2016 reversed the development. Click picture to enlarge.
The findings have been apparent. In the graph, above, even through the downtrend there’s a almost flat variety of guests per web page (see the decrease, yellow line). But the pages that acquired visitors (proven within the blue line) dramatically dropped.
This key knowledge evaluation and visualization saved priceless time. I didn’t want to take a look at content material points, however, as an alternative, I might give attention to indexing. We have been capable of affirm indexing issues whereas taking a look at Index Status in Google Search Console, as proven under.
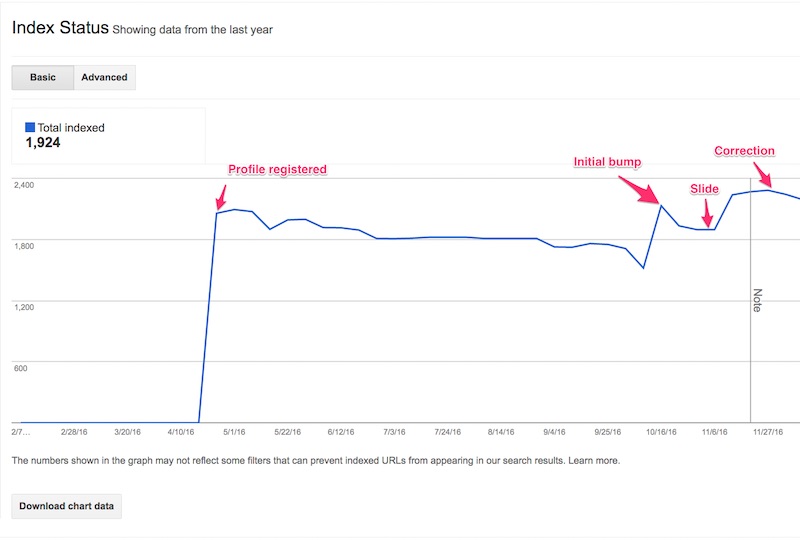
Note an preliminary bump in listed pages when the brand new website launched, however then the next slide, and eventually the correction bump at first of November. Click picture to enlarge.
Next, we would have liked to find out why Google was dropping pages. So we appeared into Google Search Console URL parameters — Search Console > Crawl > URL Parameters — to seek out indications of an infinite crawl area.
That matter, infinite crawl areas, deserves an evidence. Infinite crawl areas typically seem in web sites with in depth databases — resembling most ecommerce platforms — and causes search-engine robots to proceed fetching pages in an countless loop. An instance of that is faceted or guided navigation, which may produce a close to limitless variety of choices. Infinite crawl areas waste Googlebot’s crawl finances, and will forestall indexing of essential pages.
In this instance, nevertheless, we didn’t have an infinite crawl area. If we did, we might see parameters with much more URLs than realistically exist on the location.
We then checked the 404 errors in Google Search Console, at Search Console > Crawl > Crawl Errors. We have been stunned to see URLs as 404 errors that we had appropriately mapped. We clicked on the pages reported as errors, and as we anticipated the right pages redirected and loaded appropriately. They didn’t look like 404 errors.
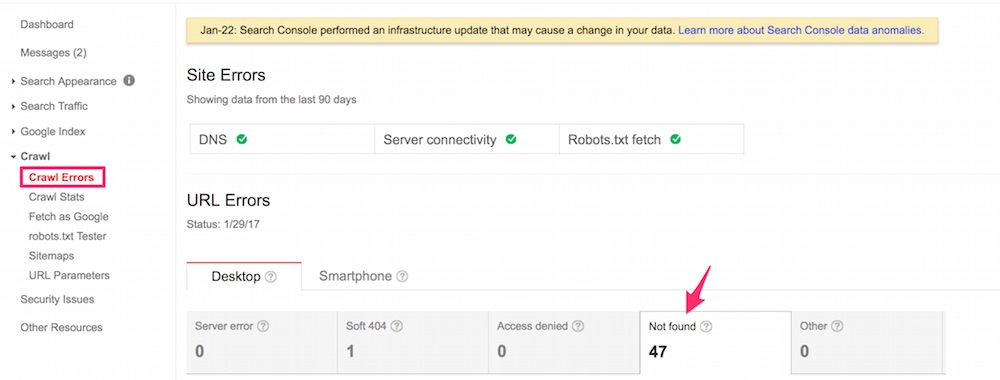
Google Search Console reported URLs as 404 errors that had been appropriately mapped. Click picture to enlarge.
I then opened Google Chrome Developer Tools to repeat the identical check. But, this time I checked the response from the online server. Bingo! The web page loaded with the fitting content material, however it reported to browsers and search engines that it was not discovered.
Google “protects” 404 pages for twenty-four hours. After that they’re dropped from the index. We labored with the event firm, which corrected the standing codes. Later, we additionally discovered one other drawback with the redirects the place they weren’t preserving redundant parameters from the previous URL, which impacts paid search monitoring and different marketing initiatives. All points have been promptly resolved. After ready for Google to re-crawl the location, the natural visitors started to extend. Ultimately, natural visitors was properly above 2015 ranges.
In brief, in case you are experiencing a downtrend in natural search visitors, don’t panic. Adopt a scientific framework, corresponding to I’ve described on this publish. Isolate the broad purpose for the decline, after which begin investigating, to repair the issue.


